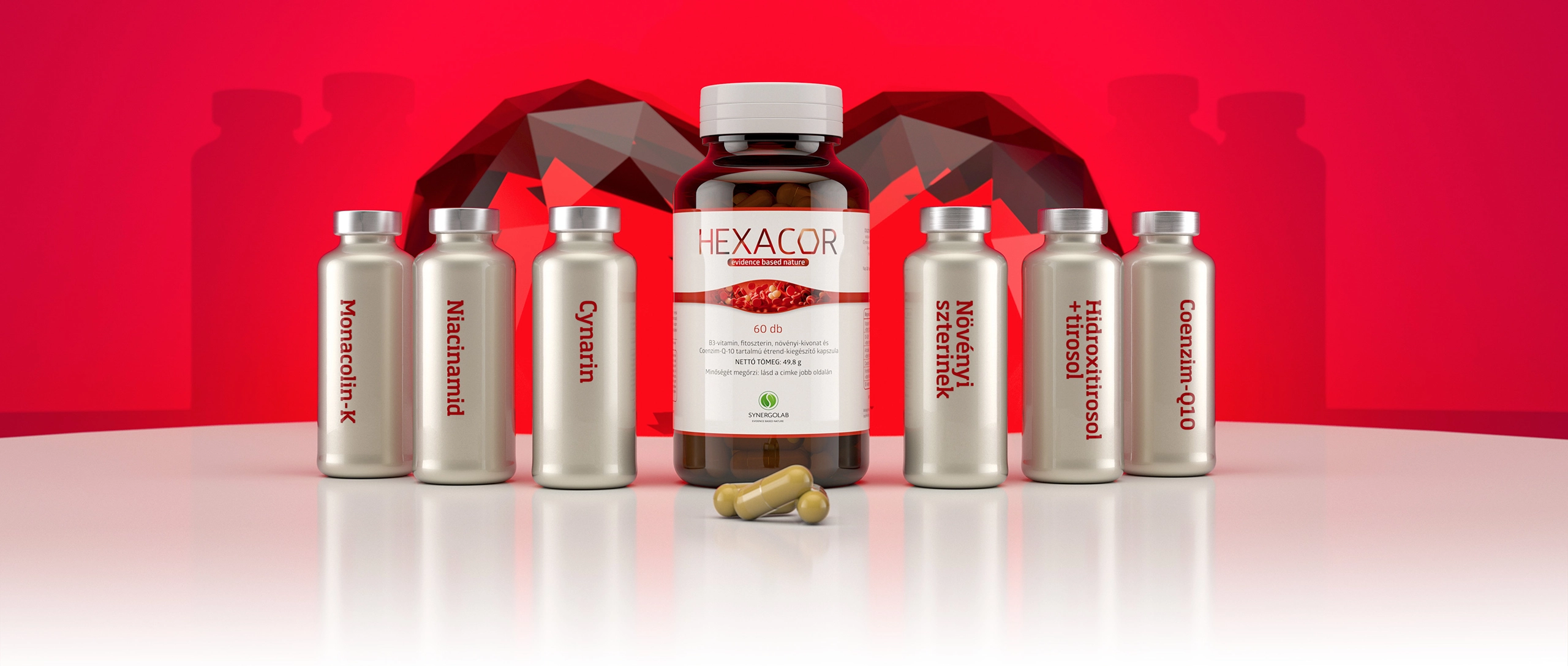

Hexacor™ dietary supplement hard capsules
Hexacor™ dietary supplement hard capsules

The product is only recommended for people
who wish to lower their blood cholesterol level.
Who is Hexacor™ recommended for? Learn more >
Only ingredients with good clinical
results, in a single capsule.
Who is Hexacor™ recommended for? Learn more >
Premium-quality formula for safe and
continuous application.
Learn more about the dosage of Hexacor™. >
A scientifically designed preparation which focuses on the
expected synergistic effect of the ingredients used.
Learn more >

Ingredients
read detailed information
about the ingredients of Hexacor™ below
hydroxytyrosol
LDL oxidation

Olive oil polyphenols help protect blood lipids against oxidative stress. EFSA
Scientists studying the statistics of the prevalence of diseases noted that in western Asia and the Mediterranean, where people have consumed olives and the oil pressed from them for thousands of years, the incidence of cardiovascular diseases is much lower than in areas where their consumption is less regular. This prompted research to identify which compounds were responsible for the positive effect. It was revealed that olive oil contains many active ingredients. It transpired that the polyphenols in olive oil help protect blood lipids against oxidative stress and, of these, hydroxytyrosol has been shown to be the most efficacious.
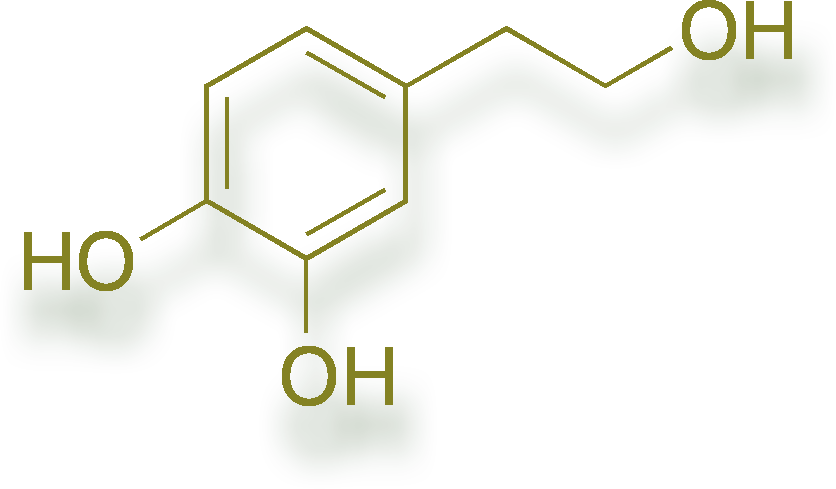
Oli-Ola™ is a completely natural olive extract produced organically from unique ancient olive trees in the southern Mediterranean region and contains 3% hydroxytyrosol. As a result of scientific studies conducted with Oli-Ola™, the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has officially declared that ‘a cause and effect relationship has been established between the consumption of olive oil polyphenols (standardised by the content of hydroxytyrosol and its derivatives) and the prevention of oxidative damage to LDL particles’. It has been demonstrated that its hydroxytyrosol content, thanks to its antioxidant activity, is able to prevent the oxidation of LDL-cholesterol (‘bad cholesterol’), thereby increasing the amount of functional HDL-cholesterol (‘good cholesterol’), which, as we know, is a highly important component in the prevention of atherosclerosis.
monacolin-K
LDL synthesis

Monacolin-K helps maintain normal blood cholesterol levels. EFSA 1648
To produce red rice, the washed and cooked rice is fermented using a yeast called Monascus purpureus. 1.2 g of fermented red rice contains about 5 mg of monacolin. The main active substance is monacolin-K. This has the same mode of action as garlic, artichokes and statins, i.e. it inhibits HMG-CoA reductase and also reduces cholesterol synthesis in HepG2 cells. 1 The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has approved the following health claim for monacolins: "monacolin K from red rice contributes to the maintenance of normal blood cholesterol levels"
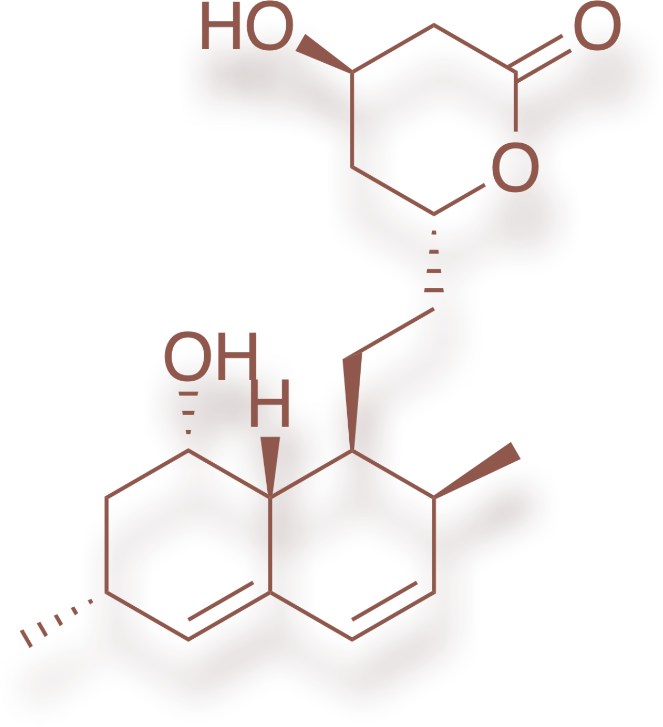
In clinical trials, cholesterol levels were significantly reduced in HepG2 cells treated with cholestin. This was associated with a reduction in cholesterol synthesis and a reduction in the secretion of both esterified and non-esterified cholesterol. Some sources suggest that the interaction of other components of fermented red rice may also be involved in lowering cholesterol levels. These may reduce the absorption of cholesterol from food and increase its excretion. 1
Medical school textbooks cited:
1 Debreceni Egyetem, Szemelvények a fitofarmakológia és fitoterápia tárgyköréből, Orvos és Egészségtudományi Centrum Gyógyszerésztudományi Kar Gyógyszerhatástani Tanszék, Dr. Juhász Béla, 2011
cynarin
excretion

The artichoke is a medicinal plant that is safe to use.
The artichoke is a Mediterranean food plant of African origin, whose medicinal importance has been known since the 20th century. The unopened bud is used for nutritional purposes, while the leaves have medicinal properties. The most characteristic compounds in artichokes are caffeic acid derivatives. 1 These substances belong to the group of polyphenols. The main active substance is considered to be cynarin. Since the 1950s, synthetic cynarin has been used to stimulate the liver and gallbladder and to treat elevated cholesterol levels.

According to the cited academic textbooks, the artichoke has been observed to have the effect of reducing cholesterol, which is attributed to enhancing bile secretion and inhibiting cholesterol synthesis (inhibiting HMG-CoA reductase). 1 Research indicates that the flavonoids found in artichokes may exhibit antioxidant activity, which is why their regular consumption is recommended, and their extracts may be a useful dietary supplement. Other studies have shown that artichoke extract may promote the conversion of cholesterol into bile salts and their excretion by increasing bile production. 1 In view of this, the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has included in its list the following health claims, which currently have on-hold status: ”(olive leaves and) artichoke leaves help to the maintain a normal cholesterol level.” EFSA ONHOLD 4597
Medical school textbooks cited:
1 Semmelweis Egyetem, Gyógynövény és Drogismeret Farmakognózia – Fitokémia, gyógynövények alkalmazása, III.2.2 FENOLOIDOKAT TARTALMAZÓ NÖVÉNYI DROGOK, Dr. Szőke Éva, egyetemi tanár (szakmai vezető), Semmelweis Egyetem, Balázs Andrea, Blázovics Anna, Kéry Ágnes, Kursinszki László, Lemberkovics Éva, Then Mária, dr. Alberti-Dér Ágnes, Balogh György, dr. Bányai Péter, Blazics Balázs, Böszörményi Andrea, Kalász Huba, Könczöl Árpád, Lugasi Andrea, Szarka Szabolcs, Szentmihályi Klára, Vasas Gábor (2012)
plant sterols
1cholesterol absorption

Plant sterols (phytosterols), stanols, stanol esters
Plant sterols are natural constituents of vegetable oils and vegetable oil-based margarines and are found in the seeds of cereals, oilseeds and vegetables. 1 Their structure is related to that of cholesterol, and so they play a similar role in plants to that of cholesterol in humans, i.e. they maintain the structure and function of the cell membrane. 1 Current knowledge suggests that they have a competitive relationship with cholesterol, which is considered a risk factor for cardiovascular diseases, in terms of absorption in the human body. Accordingly, an increased intake of phytosterols may reduce the level of cholesterol in the blood. 2
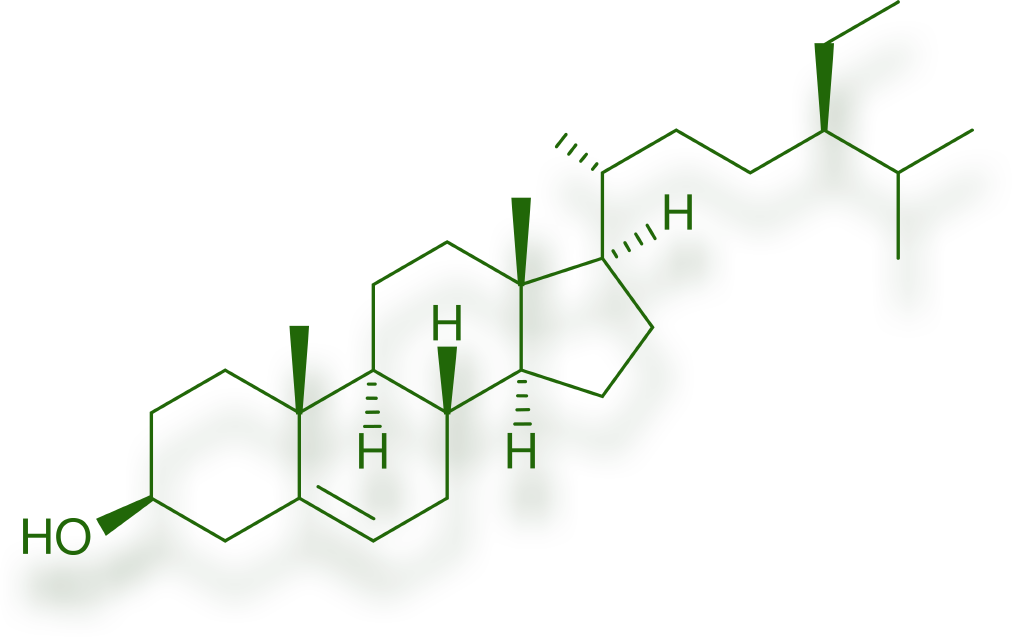
Not all the details of the mechanism of action of plant sterols in reducing cholesterol are known, but one of the essential factors is inhibiting the absorption of cholesterol in the gut. The combined effects result in less cholesterol being absorbed and more being excreted, while almost all of the plant sterols are excreted. 2 The liver compensates for the reduced cholesterol absorption by increasing cholesterol synthesis, but total and LDL-cholesterol levels fall, while HDL-cholesterol and triglyceride concentrations remain unchanged. 2 In recognition of the research findings, the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) included in its list and approved the following health claim: ”plant sterols/stanols contribute to the maintenance of normal blood cholesterol levels.”
Academic literature cited:
1 Corvinus Egyetem, Élelmiszer tudományi kar, DOKTORI ÉRTEKEZÉS, Aktív anyagok szerepe rozmaring ízesítésű napraforgó olajban, Somogyi László 2008 2 A növényi szterinek hatékonysága a szérum koleszterinszint csökkentésében Dr. Császár Albert írása
coenzyme Q10,
cellular respiration
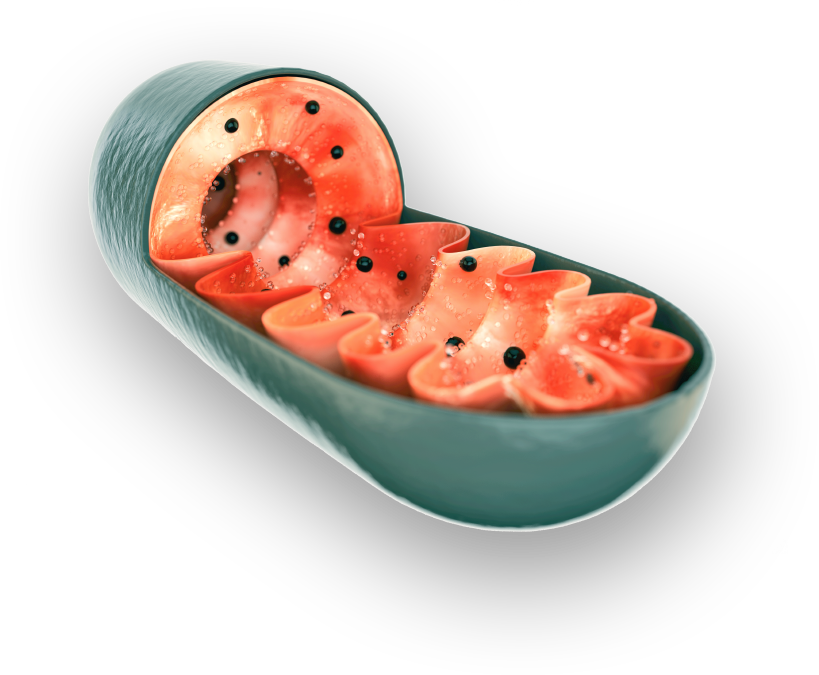
Coenzyme Q10 plays a vital role in the energy production processes of cells
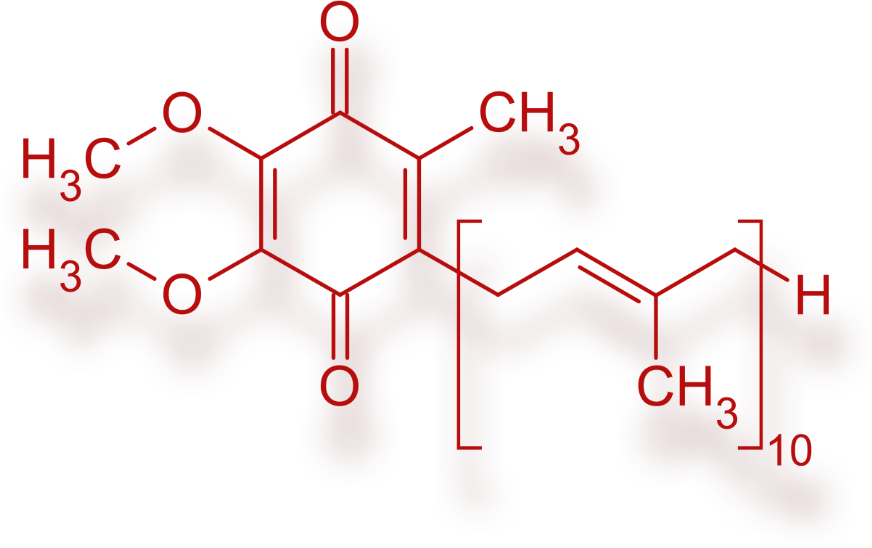
Coenzyme Q10 (ubiquinone, ubidecarenone) is an important antioxidant and a crucial molecule in the mitochondrial energy production process 1. Coenzyme Q10 levels are reduced in the myocardium, especially in hyperlipidaemia, which adversely affects the ischaemic tolerance of the heart. The use of coenzyme Q10 in preparations with subtherapeutic doses as dietary supplements is widespread. The therapeutic dose of the preparations is 100-200 mg per day. 1 Coenzyme Q10 is important for all cells, but especially for energy-intensive cells. Coenzyme Q10 levels decline rapidly after the age of 40. 1
Statins and coenzyme Q10
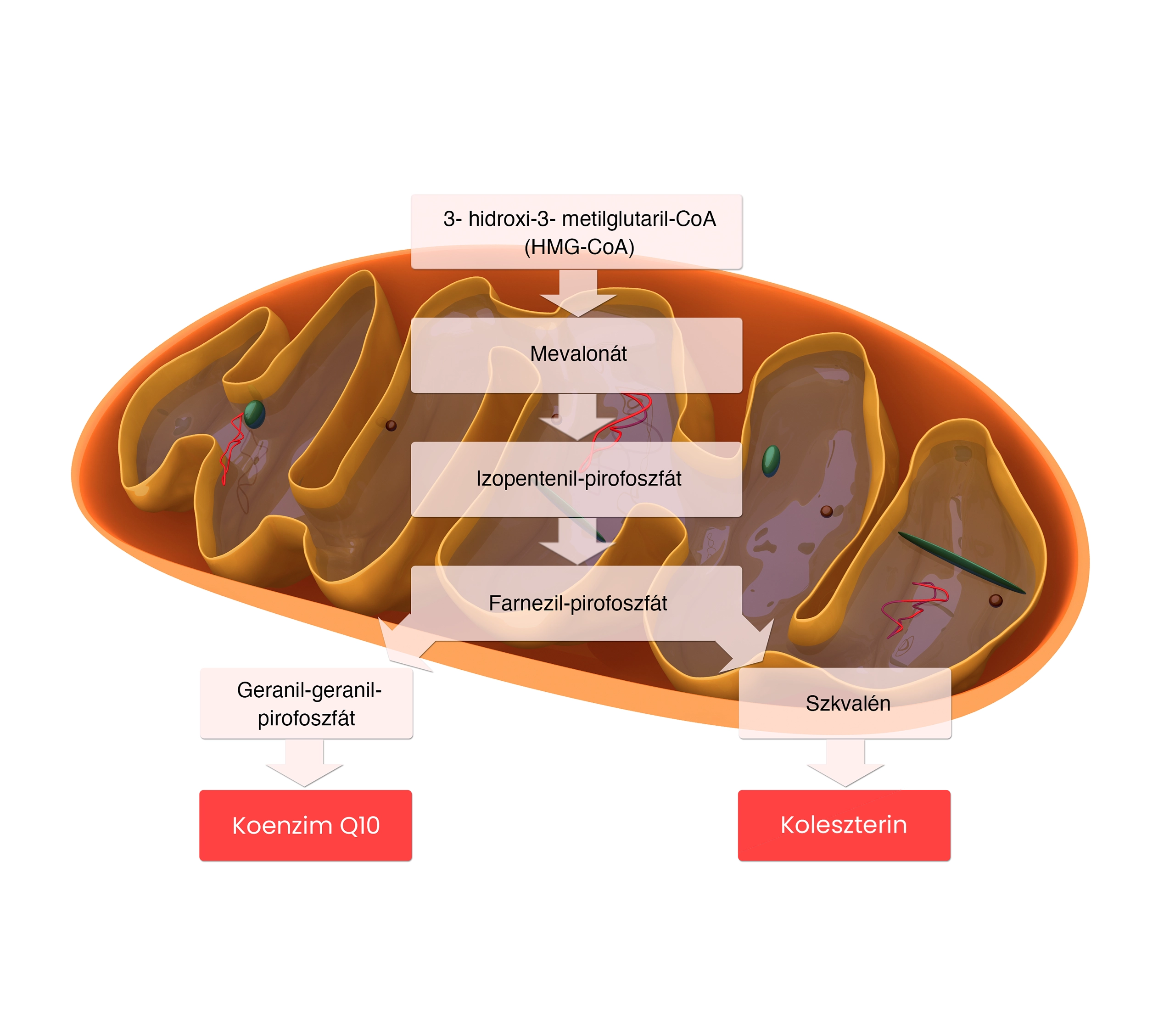
In the body, the enzyme HMG-CoA reductase catalyses the rate-determining step in the biochemical process of cholesterol synthesis. The advent of statins, which are specific competitive inhibitors of enzyme activity, has revolutionised the medically assisted treatment of diseases accompanied by high cholesterol levels. 3 It has been observed that inhibiting HMG-CoA not only leads to a reduction in cholesterol synthesis. Because cholesterol and coenzyme Q10 are formed from the same precursor, inhibiting the enzyme that is the target of statins can result in a significant reduction in coenzyme Q10 levels. 2
Medical school textbooks cited:
1 Gyires Klára - Fürst Zsuzsanna: A farmakológia alapjai, 2011: 232-246.258-287., Semmelweis Egyetem
2 Gyires Klára - Fürst Zsuzsanna: A farmakológia alapjai, 2011, III. A szív, az érrendszer és a vese gyógyszertana: 230., Semmelweis Egyetem
3 Semmelweis Egyetem Gyógyszerésztudományok Doktori Iskola Kolloidok a kontrollált farmakon-transzport szabályozására: Süle András, 2009. 25.
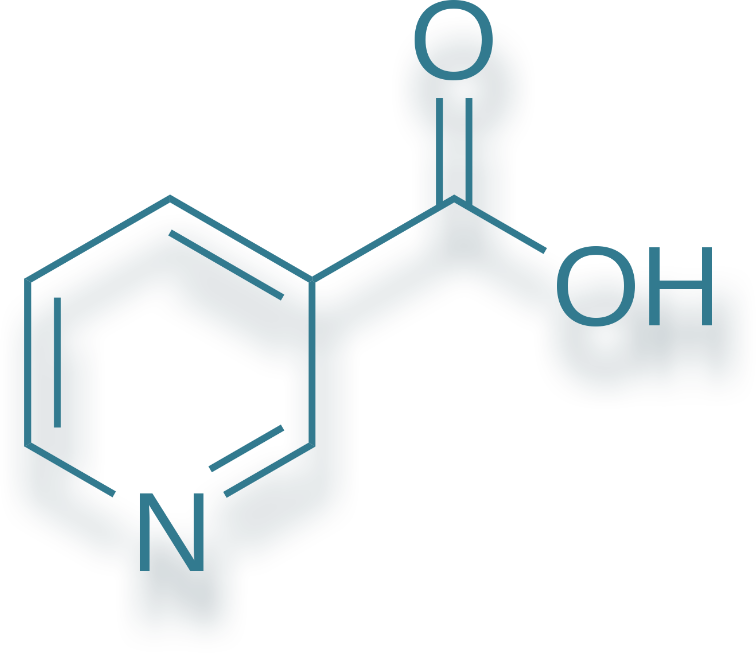
Vitamin B3 (niacin),
energy expenditure

Niacin is involved in normal energy-yielding metabolic processes. EFSA
According to the latest edition of the pharmaceutical science textbooks used in Hungarian medical education today: "Niacin (vitamin B3, nicotinic acid) is the oldest agent for treating dyslipidaemia and has a beneficial effect on all lipid parameters. Niacin is effective in reducing VLDL, LDL and Lp(a) levels and raising HDL levels. Nicotinic acid is converted to nicotinamide in the body and, performing the vitamin function, is incorporated into NAD. Nicotinamide does not affect lipoprotein levels. 2 Niacin is almost entirely absorbed, having a half-life in serum of about an hour, thus two to three doses a day may be needed. The liver absorbs niacin but, with higher doses, some of the nicotinic acid is excreted in urine in an unchanged form." 2
According to data from pharmacology textbooks, niacin activates lipoprotein lipase, inhibits the secretion of VLDL, and thus reduces chylomicron, VLDL and triglyceride levels. It reduces the breakdown of HDL through the mediation of ApoA and thus raises HDL cholesterol levels. 2 It is thought to reduce the activity of hormone-sensitive lipase in adipose tissue and thus lower the flow of free fatty acids to the liver, which leads to a reduction in triglyceride and VLDL synthesis. 1 A harmless side effect is flushing caused by dilated skin vessels, which can be prevented by gradually increasing the dose and taking aspirin with the first few doses. 2
Medical school textbooks cited:
1,2 Semmelweis Egyetem, Az orvosi élettan tankönyve, Fonyó, Attila, 2011
Hexacor™™ is a registered trademark of SynergoLAB.
Copyright © 2022 SynergoLAB Inc. All rights reserved.